Can You Test Yourself for Diabetes? Everything You Need To KnowCan You Test Yourself for Diabetes? Everything You Need To Know
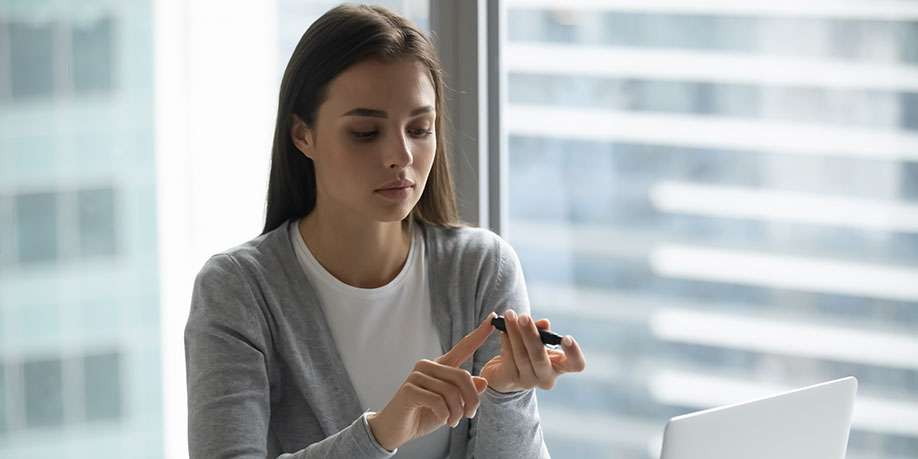  © Fizkes | Dreamstime.com It might be challenging to find out if you are diabetic. Diabetes can reveal itself in different ways and you have to know its symptoms to start worrying about your health. There are several types of diabetes that are different in their nature and caused by different problems in the body. But all types of diabetes have one thing in common – they affect how the body processes sugar (glucose) that we get from food to provide energy to the body cells. If you are diabetic, your body doesn’t process sugar properly and sugar accumulates in your blood. High level of sugar in your blood can cause many serious and even life-threatening health issues, including blood vessel disease, increased risk of heart attack and stroke, nephropathy (kidney damage), eye damage (including blindness), pregnancy complications, sleep apnea, nerve damage (neuropathy), Alzheimer’s disease, fungal or bacterial infections, and feet damage that can lead to amputation. All that makes one thing about diabetes certain – the earlier it gets diagnosed and starts getting managed, the less impact the disease can make to the body. And to diagnose diabetes, you need to get tested. But how to figure out if you need to get tested? There are several symptoms that are tell-tale signs that you might have developed diabetes. Among those symptoms are extreme thirst, excessive hunger, need to urinate frequently, irritability and fatigue, nausea and vomiting, blurred vision, rapid breathing, unexplained weight loss, tingling sensation and numbness in the feet and hands, dry skin and mouth, and slow healing of cuts and wounds. There are also certain risk factors that can increase your risk of getting diabetes, such as having high blood pressure, being obese or overweight, having history of heart disease or stroke, being 45 years of age or older, having little or no physical activity, having low level of “good” (HDL) cholesterol and high level of triglycerides, and having polycystic ovary syndrome and history of gestational diabetes. So what to do if you feel that you have developed symptoms of diabetes? – It is time to visit your doctor to do blood glucose tests. There are several tests that your doctor may perform to diagnose diabetes and it usually takes multiple tests of the following ones to confirm diagnosis and determine the type of diabetes: Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG) test that is taken in the morning after overnight fasting; Oral Glucose Tolerance test (OGTT), when blood sugar is measured two hours after you drink 75 grams of glucose – it is most commonly used during pregnancy; Random blood glucose test; and Hemoglobin A1C (glycohemoglobin) test that measures the average glucose level over the period of past 2-3 months. Besides, test can be done on your urine for glucose and for chemicals that your body produces when your insulin level is insufficient. You may also test yourself for diabetes at home before going to the doctor. There are two non-prescription blood sugar tests widely available – At Home A1C Test Kit and urine test strips. Similarly to a lab Hemoglobin A1C test, the A1C home test can measure your average blood sugar levels over the past 3 months. The kit is comprised of a blood-drawing device (a lancet) and a monitor. The testing process comes down to pricking your finger with a lancet, collecting the blood, and inserting it into the monitor to get the blood test result. Urine test kits usually include up to 3 strips with a special coating. When a strip is inserted into a urine sample, it turns a certain color that corresponds to the detected blood sugar level. Although the A1C home test and the urine test strips have been widely used for self-diagnosis purposes, they are only intended for monitoring blood glucose levels in people who are already diagnosed with diabetes. If you have been diagnosed with diabetes, you have to test your blood sugar level at home on a daily basis, in some cases, several times a day. Knowing the results allows you to take proper actions to keep diabetes under control. There are several ways to monitor your blood sugar. You can use traditional home glucose monitoring, that involves drawing blood from your finger with a lancet, putting a small drop of blood on a testing strip, and then inserting the strip into the meter to see your blood sugar level. Another option is to utilize meters that test other parts of the body, such as forearm, upper arm, thumb, or thigh. You can also utilize a continuous glucose monitoring system (CGM) – a small medical device that continuously monitors your blood sugar levels in real time. Such devices are often combined with insulin pumps to automatically regulate your blood sugar level. A CGM system consists of a small sensor equipped with a cannula that penetrates your skin. The sensor is attached to your abdomen with an adhesive patch. A reusable transmitter is connected to the sensor to wirelessly send real-time test results to a display device. Diabetes is a very serious condition that can dramatically affect a person’s life if not taken under control early enough. For that you should know the symptoms of the disease to identify it and then conduct certain tests to confirm the diagnosis. Although it’s more preferable to be tested by a healthcare professional, people still have an option to test their blood sugar level at home, which helps them to plan further actions and treat the disease in its earliest stages.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||